南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 董强)近日,我校水产学院高泽霞教授课题组在Aquaculture期刊上在线发表了题为“Generation of Megalobrama amblycephala without intermuscular bones by runx2b gene mutation”的研究论文。该研究获得了肌间刺完全缺失且生长发育正常的团头鲂F1代突变个体,不仅为获得可稳定遗传的团头鲂新品种奠定了重要基础,也为无肌间刺性状从模式物种到经济鱼类上的应用提供了很好的示例。
肌间刺起源于肌腱祖细胞,膜内骨化而来,仅存在于低等真骨鱼类中。世界主要养殖鱼类都含有一定数量的肌间刺,特别是我国主养的青草鲢鳙鲤鲫鲂等大宗淡水鱼类,食用时极易出现卡喉咙的危险,严重影响了其水产品的经济价值。课题组前期以模式鱼类斑马鱼为研究材料,筛选鉴定出调控鱼类肌间刺发生的关键基因runx2b,2022年发表于National Science Reivew上。接着,课题组开始探索是否可以将这一模式物种上的研究发现应用到经济鱼类上。
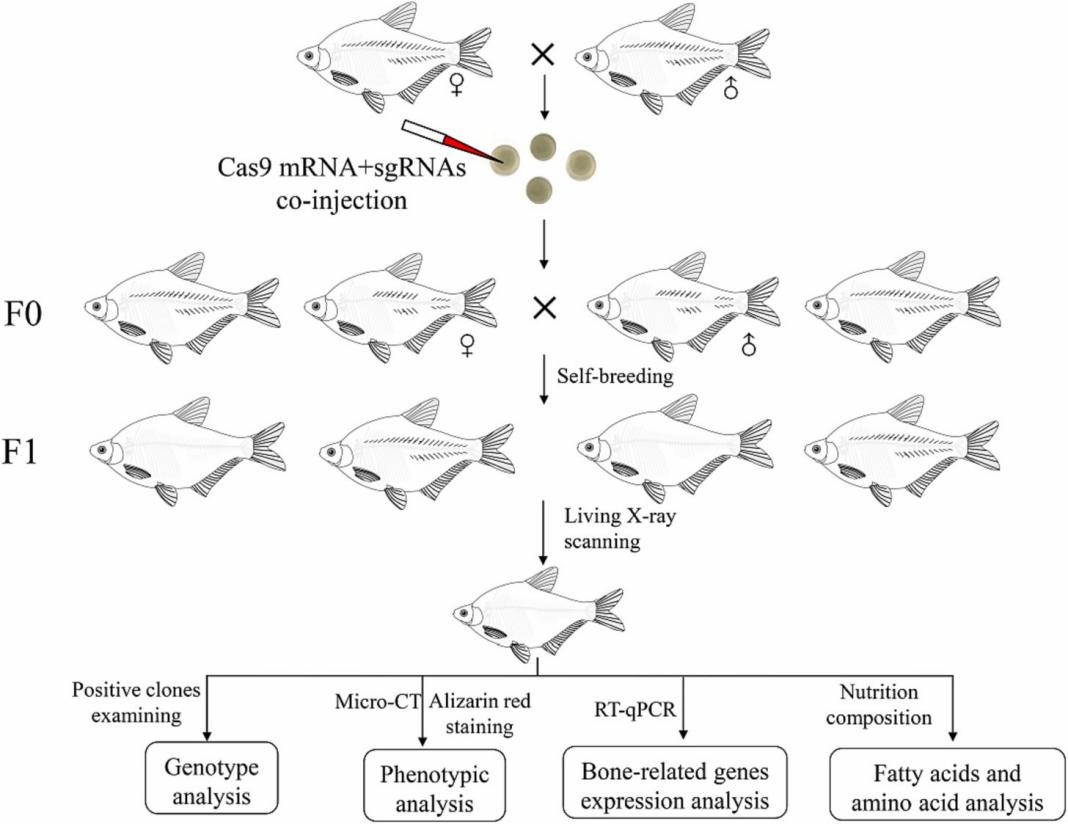
图1 F1代runx2b团头鲂突变体的获取和分析示意图
课题组以长期开展遗传选育工作的团头鲂(俗称武昌鱼)为经济养殖鱼类代表开展验证工作。团头鲂属于鲤形目、鲤科、鲌亚科、鲂属鱼类,是我国重要的淡水养殖经济鱼类,约含118根肌间刺。课题组前期已通过分子辅助选育技术培育出生长速度快、成活率高的团头鲂“华海1号”国审新品种,在该品种的基础上,采用基因编辑获得肌间刺部分缺失的团头鲂突变体F0代(肌间刺缺失5.6%–33.8%),进一步将F0代雌雄突变个体进行人工繁殖获得F1代。课题组随机筛选45天的团头鲂F1代品系60条,运用茜素红整体骨骼染色方法观察团头鲂F1代肌间刺的表型,结果显示27条团头鲂的肌间刺完全缺失。在F1代群体4月龄时,课题组利用便携式X光扫描仪在5000尾个体中筛选到了316尾完全没有肌间刺的团头鲂个体,可作为2023年繁殖无肌间刺团头鲂的亲本。同时,研究发现完全无肌间刺团头鲂F1代幼鱼个体骨骼的矿化、肌肉脂肪酸和氨基酸含量等性状均未受到显著影响。目前,无肌间刺团头鲂生长性状良好,6月龄无刺团头鲂平均体重达到了150g以上,部分个体已达到250 g。课题组后期将进一步跟踪研究无肌间刺团头鲂成鱼的骨骼矿化、肌肉营养成分等性状差异情况。
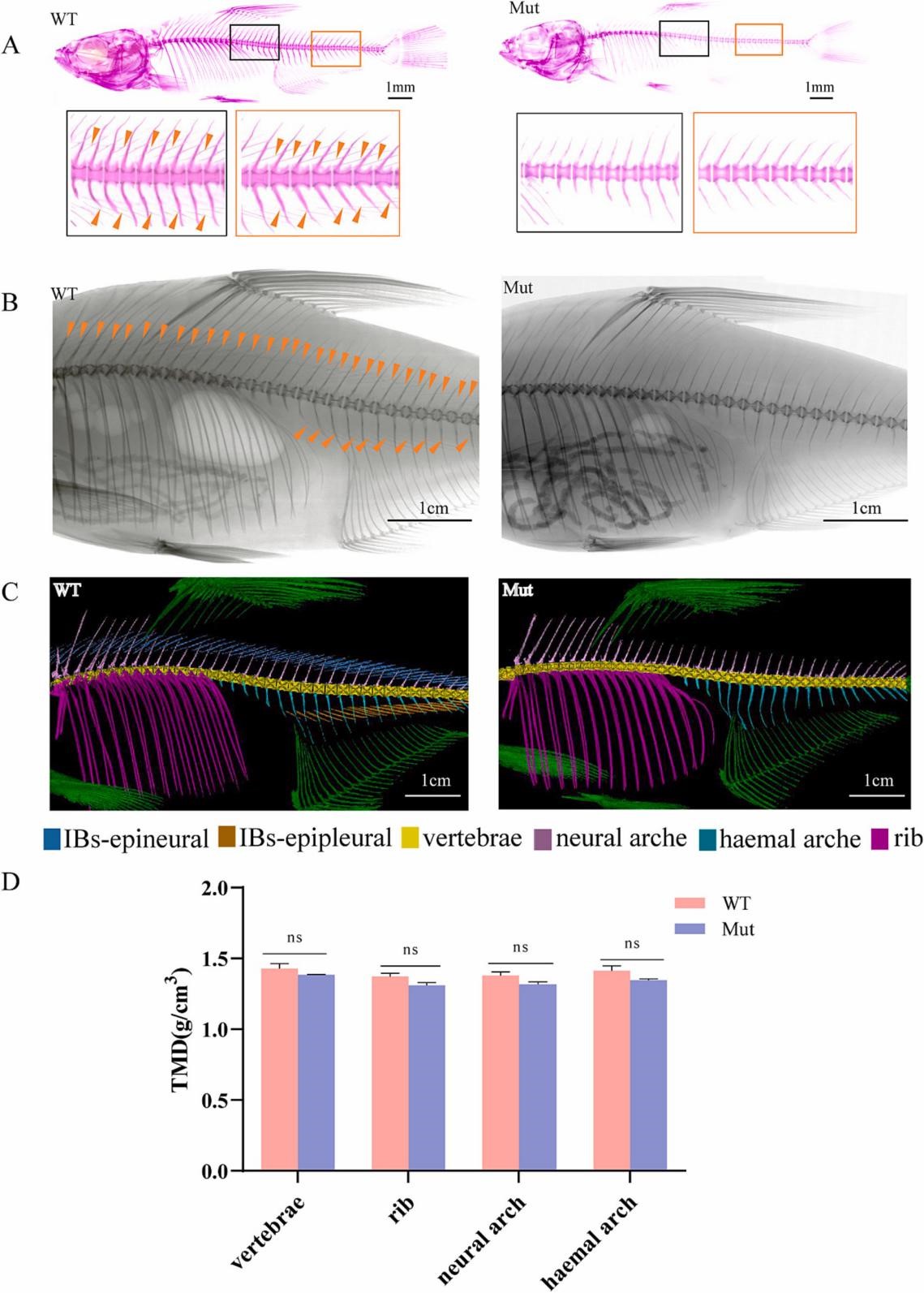
图2. 团头鲂野生型和runx2b突变体的表型。A, 45dpf 茜素红骨骼染色结果图;B, 120dpf X射线扫描结果图;C, 120dpf micro-CT扫描结果图;D, 四种不同骨骼元素的组织矿物质密度(TMD)值。ns,P>0.05; ∗,P<0.05。
我校水产学院硕士生董强和博士后聂春红为论文共同第一作者,水产学院高泽霞教授为论文通讯作者。该研究得到国家大宗淡水鱼类产业技术体系、湖北洪山实验室、国家自然科学基金、国家重点研发计划等项目的支持。
审核人:高泽霞
【英文摘要】
Blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) is an important herbivorous freshwater economic fish cultivated in China. Its economic value has been affected by the existence of intermuscular bones (IBs). Our previous study proved that runx2b is the key gene for the IBs formation, and lack of runx2b gene could obtain a stable zebrafish mutant without IBs. We found runx2b mutant F0 generation of blunt snout bream through CRISPR/Cas9 editing technology had a significant reduction on the number of IBs. In order to further obtain the blunt snout bream without IBs, we used the runx2b mutant F0 generation to self-bred to obtain F1 generation. Subsequently, the 35 runx2b mutant F1 individuals of blunt snout bream without IBs were genotyped and found the number of runx2b targeting sites 1, 2 and 3 obtained 3 (1 insertion, 2 deletion), 13 (8 insertion, 5 deletion) and 7 (1 insertion, 6 deletion) mutation types with the mutation efficiency being 25.71%, 94.28%, and 71.43%, respectively. Alizarin red bone staining and X-ray scan analysis showed that IBs were not existed in runx2b mutant F1 individuals, and micro-CT analysis found that the mineralization of other bone in runx2b mutant was not significantly affected compared to wild type fish (P > 0.05). RT-qPCR results also exhibited that bone-related genes had a lower expression level in runx2b mutants compared to wild type fish. Subsequently, we used the national standard methods to detect nutrition composition of muscle tissue in wild type (with IBs) and runx2b mutant F1 individuals (without IBs) at 120 dpf. The results showed that the basic muscle nutritional composition (moisture, crude protein, crude lipid and crude ash), and the contents of most amino acids and fatty acids had no significant differences between wild and runx2b mutant at juvenile stage (P > 0.05). This study proves that the runx2b gene has an essential role for IBs formation in aquaculture species and lays an important foundation for obtaining a new blunt snout bream strain without IBs, which provides a good example for the application of IBs-free characters from model fish to commercial fish.
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739263
Blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) is an important herbivorous freshwater economic fish cultivated in China. Its economic value has been affected by the existence of intermuscular bones (IBs). Our previous study proved that runx2b is the key gene for the IBs formation, and lack of runx2b gene could obtain a stable zebrafish mutant without IBs. We found runx2b mutant F0 generation of blunt snout bream through CRISPR/Cas9 editing technology had a significant reduction on the number of IBs. In order to further obtain the blunt snout bream without IBs, we used the runx2b mutant F0 generation to self-bred to obtain F1 generation. Subsequently, the 35 runx2b mutant F1 individuals of blunt snout bream without IBs were genotyped and found the number of runx2b targeting sites 1, 2 and 3 obtained 3 (1 insertion, 2 deletion), 13 (8 insertion, 5 deletion) and 7 (1 insertion, 6 deletion) mutation types with the mutation efficiency being 25.71%, 94.28%, and 71.43%, respectively. Alizarin red bone staining and X-ray scan analysis showed that IBs were not existed in runx2b mutant F1 individuals, and micro-CT analysis found that the mineralization of other bone in runx2b mutant was not significantly affected compared to wild type fish (P > 0.05). RT-qPCR results also exhibited that bone-related genes had a lower expression level in runx2b mutants compared to wild type fish. Subsequently, we used the national standard methods to detect nutrition composition of muscle tissue in wild type (with IBs) and runx2b mutant F1 individuals (without IBs) at 120 dpf. The results showed that the basic muscle nutritional composition (moisture, crude protein, crude lipid and crude ash), and the contents of most amino acids and fatty acids had no significant differences between wild and runx2b mutant at juvenile stage (P > 0.05). This study proves that the runx2b gene has an essential role for IBs formation in aquaculture species and lays an important foundation for obtaining a new blunt snout bream strain without IBs, which provides a good example for the application of IBs-free characters from model fish to commercial fish.