南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 胡亚珍)我校国家特色淡水鱼产业技术体系细菌病防控岗位科学家张永安教授领衔的鱼类免疫与病害防控团队长期关注鱼类免疫效应因子的发掘与功能研究,以期高效利用免疫效应因子防控鱼类病害。近来,团队从比较免疫学的视角系统探究了细胞因子LECT2和补体分子C3a、C4a和C5a的抗菌活性、抗菌机制及其演化规律,研究结果相继发表于免疫学经典期刊Journal of Immunology(2022a,2022b,2023),授权国家发明专利两件。
研究团队通过整合凝胶过滤层析、离子交换层析和质谱鉴定技术,从草鱼肠道中分离并鉴定出一个新型抗菌蛋白——白细胞衍生趋化因子2(LECT2)。发现LECT2除了具有之前报道的免疫调节活性,在低等脊椎动物中还具有直接杀菌活性和凝集细菌的活性,从而帮助宿主抵御病原菌的感染。与四足动物不同,硬骨鱼类的LECT2发生了基因复制和演化,其中LECT2-a主要表达于系统免疫器官中,而LECT2-b则主要表达于黏膜免疫器官中(Hu et al., Journal of Immunology, 2022a)。进一步研究发现LECT2-b能够调控宿主肠道菌群稳态,敲降LECT2-b表达则会导致肠道菌群紊乱,条件致病菌含量增加,其中气单胞菌的增加尤为显著,进而引发肠道炎症;注射回补LECT2-b重组蛋白能够减轻敲降LECT2-b导致的肠道炎症,重建肠道菌群稳态。进一步研究表明,带正电荷的LECT2-b会优先靶向和杀伤带较多负电荷的病原菌而非益生菌,这可能是LECT2-b能够调控宿主肠道菌群稳态的重要机制(Hu et al., Journal of Immunology, 2023)。该研究系统地探究了脊椎动物LECT2,特别是硬骨鱼类的LECT2在抗菌免疫中的新功能,解析了草鱼LECT2-b调控肠道菌群稳态的功能和作用机制,为利用免疫效应因子防控鱼类细菌性疾病提供了理论依据和候选分子。
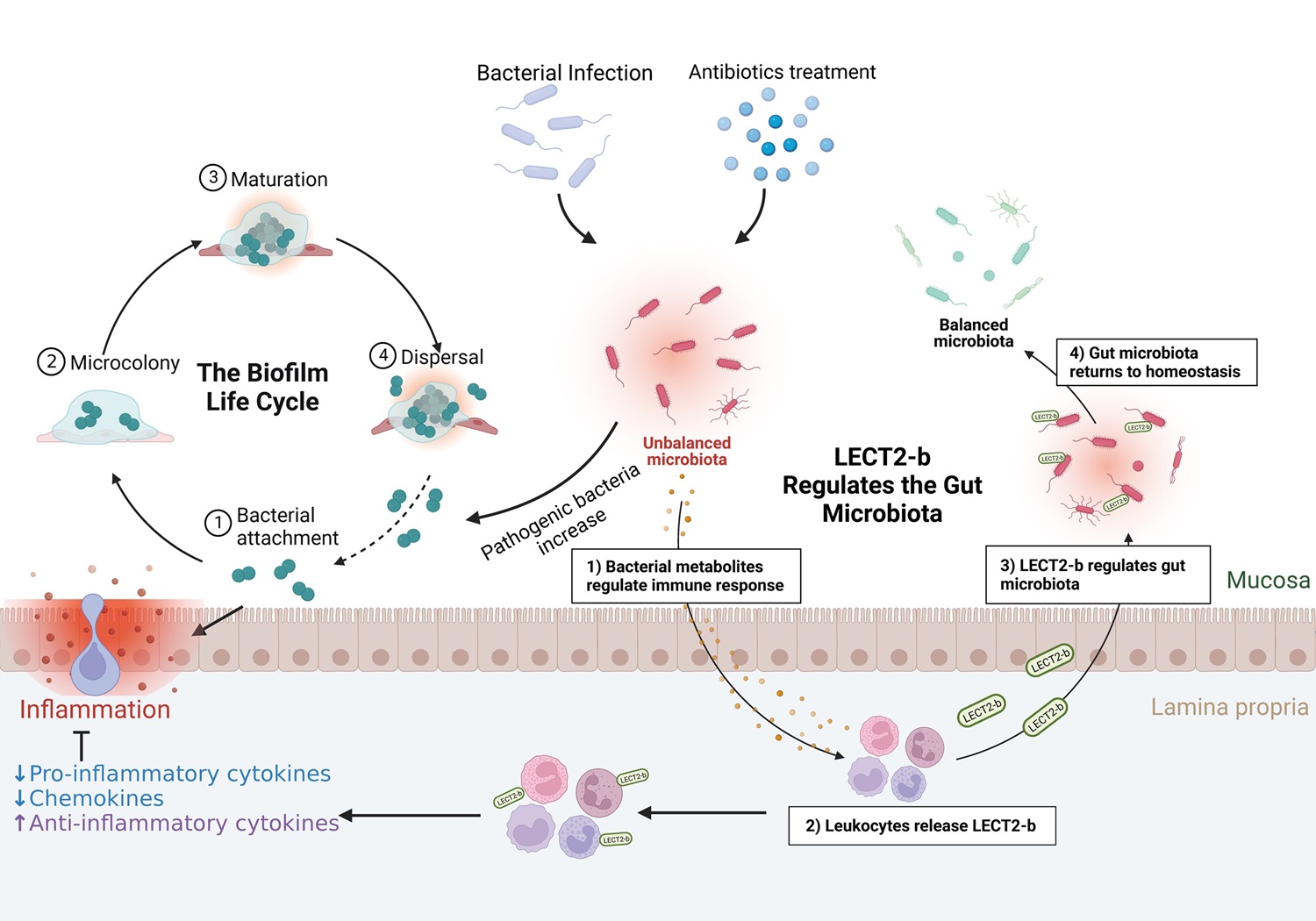
草鱼LECT2-b调控肠道菌群稳态的示意图
此外,研究团队系统探究了脊椎动物补体分子C3a、C4a和C5a的抗菌功能,发现脊椎动物C3a、C4a和C5a的结构较为保守,但所带净电荷呈现显著趋异演化,是其抗菌活性的决定因子,通过将中性或带负电荷的氨基酸点突变为带正电荷的氨基酸可以让无抗菌活性的C3a、C4a和C5a源多肽转变为抗菌肽,此研究为来源于补体分子C3a、C4a和C5a的抗菌肽的分子设计奠定了重要的理论基础(Zhang et al., Journal of Immunology, 2022b)。研究团队还发现草鱼C3a能够通过IgM+B细胞表面的受体C3aR显著促进IgM+B细胞的吞噬活性,且C3a碳末端的α-螺旋具有完整的促吞噬功能,这不仅揭示了鱼类C3a的新功能,还为通过分子设计将C3a以及C5a(均具有显著的免疫调节活性)开发为疫苗分子佐剂奠定了理论基础(Ma et al., Frontiers in Immunology, 2022)。
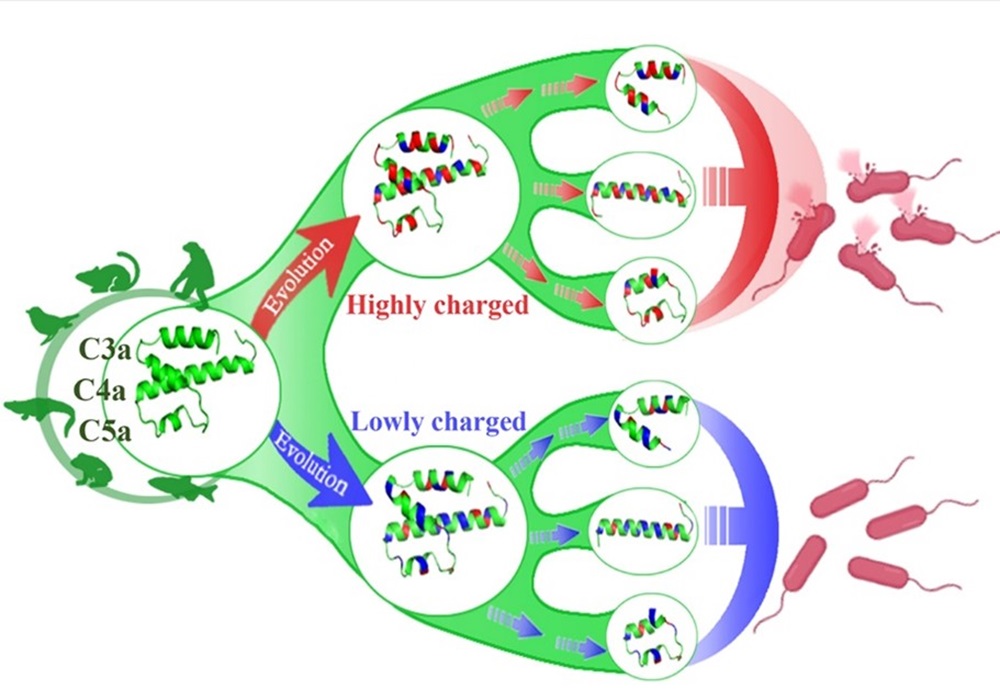
脊椎动物补体分子C3a,C4a和C5a抗菌活性趋异演化的示意图
我校水产学院已毕业博士生胡亚珍、已毕业硕士生马自有以及张旭杰副教授分别为相关论文的第一作者,张永安教授和张旭杰副教授为论文的共同通讯作者。
上述研究得到了国家重点研发计划项目、国家自然科学基金、国家现代农业产业技术体系及湖北洪山实验室重大项目等资助。
审核人:张旭杰 张永安
英文文献:
Complement C3a Enhances the Phagocytic Activity of B Cells Through C3aR in a Fish
The complement system is an important part of the immune system of teleost fish. Besides, teleost B cells possess both phagocytic activity and adaptive humoral immune function, unlike mammalian B1 cells with phagocytic activity and B2 cells specific to adaptive humoral immunity. However, the cross talk between complement system and phagocytic B cells in teleost fish still requires elucidation. Here, we show that, unlike tetrapods with a single C3 gene, nine C3 genes were identified from the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) genome, named C3.1-C3.9. Expression analysis revealed that C3.1 is the dominant C3 molecule in grass carp, for its expression was significantly higher than that of the other C3 molecules both at the mRNA and protein levels. The C3a fragment of C3.1 (C3a.1) was determined after the conserved C3 convertase cleavage site. Structural analysis revealed that C3a.1 consists of four α-helixes, with the C-terminal region forming a long α-helix, which is the potential functional region. Interestingly, we found that the recombinant GST-C3a.1 protein and the C-terminal α-helix peptide of C3a.1 both could significantly enhance the phagocytic activity of IgM+ B cells. Further study revealed that the C3a receptor (C3aR) was highly expressed in grass carp IgM+ B cells, and the phagocytosis-stimulating activity of C3a.1 could be dramatically inhibited by the anti-C3aR antibodies, indicating that C3a.1 performed the stimulating function through C3aR on IgM+ B cells. Taken together, our study not only uncovered the novel phagocytosis-stimulating activity of C3a, but also increased our knowledge of the cross talk between complement system and phagocytic B cells in teleost fish.